Introduction
Faisalabad Electric Supply Company (FESCO) is a leading power distribution company in Pakistan, serving approximately 4.01 million customers within its territory. FESCO’s operations are crucial for the socio-economic development of the region, as it ensures the delivery of reliable and cost-effective electricity to both residential and commercial sectors.
Understanding the FESCO tariff is essential for consumers to manage their energy expenses effectively. FESCO Tariffs are the prices that consumers pay for the electricity they consume, and these rates are determined based on various factors, including the type of usage (residential or commercial), the amount of consumption, and peak hours. By knowing the current tariffs and how they are applied, customers can make decisions about their energy usage, leading to potential cost savings and more efficient energy consumption patterns.
Below, we’ll discuss the FESCO Tarif rates for residential and commercial customers along with the billing process and practical tips for energy conservation.
Understanding FESCO Tariffs
Tariffs are the pricing structures set by an electricity distribution company, such as FESCO, to charge customers for their energy usage. These rates are not arbitrary; they are carefully calculated based on a variety of factors to ensure fair pricing and to cover the costs of generating, transmitting, and distributing electricity.
How Tariffs Are Determined
Cost of Production: The primary factor in tariff determination is the cost involved in producing electricity. This includes the cost of fuel, operation, and maintenance of power plants.
Return on Investment: Energy companies invest heavily in infrastructure and equipment. Tariffs must reflect a return on these investments to sustain the company’s financial health.
Regulatory Factors: Government regulations and policies can influence tariffs. Subsidies or taxes imposed by the government are taken into account.
Market Dynamics: In deregulated markets, competition can affect tariff rates. Companies may adjust tariffs to remain competitive while still covering costs.
Consumer Categories: Different tariffs for residential, commercial, and industrial consumers reflect their varying usage patterns and energy needs.
Role of Tariffs in Energy Billing
Tariffs play a critical role in energy billing, serving as the basis for calculating the amount owed by a consumer. The energy bill typically includes the following components:
Fixed Charge: A set fee that covers the cost of maintaining the electrical connection, regardless of consumption.
Energy Charge: Calculated by multiplying the number of kilowatt-hours (kWh) used by the tariff rate.
Taxes and Levies: Additional charges mandated by the government or regulatory bodies.
Fuel Price Adjustment: An adjustment to account for fluctuations in fuel prices used in electricity generation.
By understanding tariffs and their impact on energy bills, consumers can better manage their energy usage and expenses. It also allows them to identify any discrepancies in their bills and seek clarification or rectification from FESCO.
FESCO Tariff Structure
FESCO’s tariff structure is designed to cater to the diverse needs of its customers, ranging from residential to commercial entities. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the tariff categories and a comparison between residential and commercial tariffs:
Residential Tariffs
A-1 General Supply Tariff Residential: This category is for single-phase residential connections, with a fixed monthly charge and a variable energy charge based on consumption. FESCO Tarif is calculated as per the following schedule w.e.f July 1st, 2023.
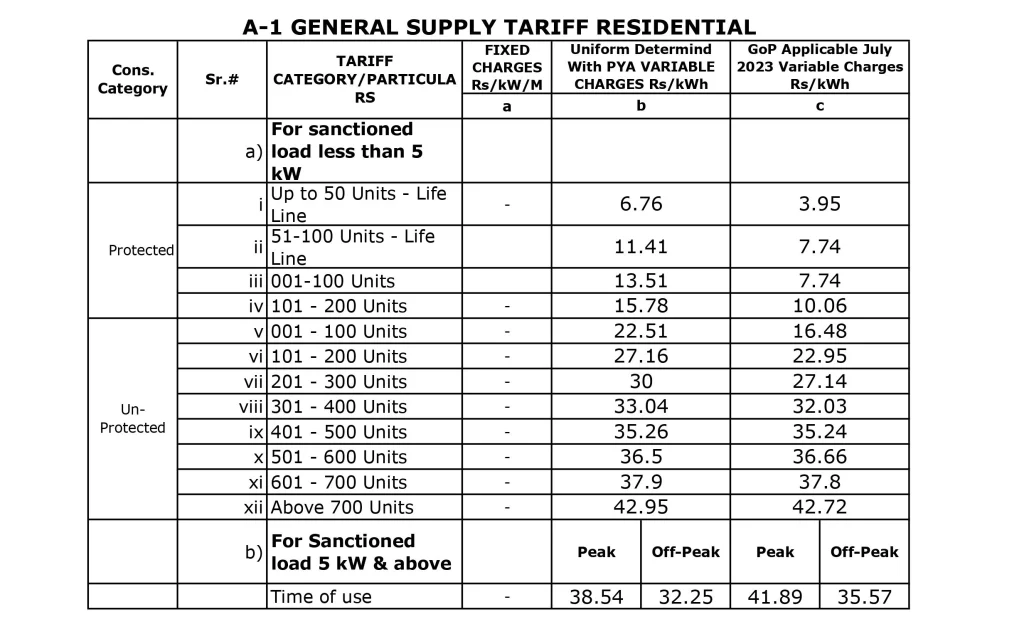
For tariff A-1, a minimum monthly customer charge is applicable regardless of energy consumption. The rates for this charge are as follows:
a) Single Phase Connections: Rs. 75 per consumer per month
b) Three Phase Connections: Rs. 150 per consumer per month
Commercial Tariffs
A-2 General Supply Tariff Commercial is Applicable to commercial offices and establishments, including shops, hotels, restaurants, and other businesses.
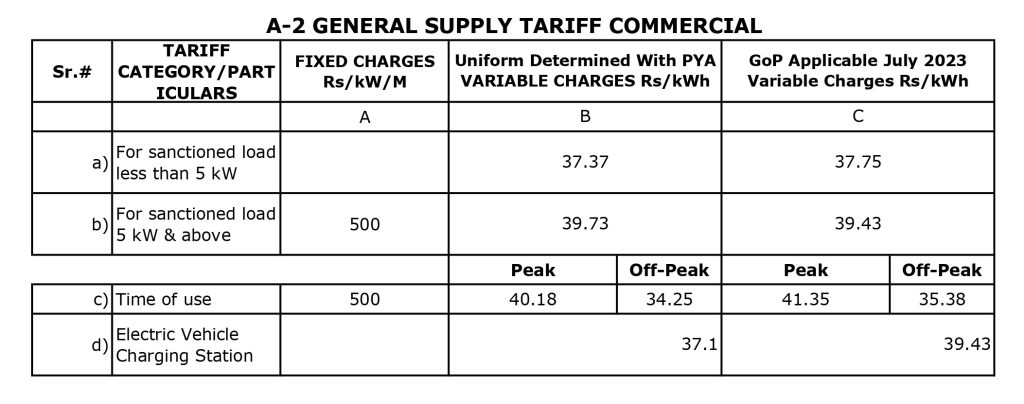
For tariff A-1, a minimum monthly customer charge is applicable regardless of energy consumption. The rates for this charge are as follows:
a) Single Phase Connections: Rs. 175 per consumer per month
b) Three Phase Connections: There are higher charges on Three Phase Connection.
c) Minimum Monthly Charges: Even if no energy is consumed, there are minimum charges applicable.
Comparison
Fixed Charges: The fixed monthly charge for commercial connections is higher than that for residential connections to reflect the higher energy demand and infrastructure requirements of commercial entities.
Energy Charges: Commercial tariffs are typically higher per unit of electricity consumed, considering the commercial operations’ extended hours and higher consumption levels.
It’s important for both residential and commercial customers to understand these tariffs to manage their energy costs effectively. For businesses, especially, optimizing energy use can lead to significant savings given the higher tariff rates.
Tips for Managing Energy Consumption
Monitor Usage: Keep track of your energy consumption, especially during peak hours.
Use Energy-Efficient Appliances: Upgrade to appliances that consume less electricity.
Insulate Your Home: Proper insulation can help maintain temperature and reduce heating and cooling costs.
Implement Smart Habits: Turn off lights and appliances when not in use and use energy-saving modes.
Guidance on Optimizing Energy Use for Businesses
Conduct Energy Audits: Identify areas where energy is wasted and where improvements can be made.
Upgrade to LED Lighting: LEDs consume less power and have a longer lifespan.
Optimize HVAC Systems: Regular maintenance and smart thermostats can lead to significant savings.
Educate Employees: Encourage energy-saving practices among staff members.
Step-by-Step Guide on FESCO Bill Calculation
Meter Reading: The billing process starts with a meter reading to determine the amount of electricity consumed during the billing period.
Billing Period: This is the timeframe for which the electricity consumption is being billed, typically one month.
Unit Consumption: The number of units consumed is calculated based on the difference between the current and previous meter readings.
Tariff Rates: The applicable tariff rates are applied to the units consumed. These rates vary depending on the customer category (residential, commercial, etc.) and the total units consumed.
Fuel Price Adjustment: This is an additional charge or credit based on fluctuations in fuel prices used for electricity generation.
Taxes and Levies: Government-imposed taxes and levies are added to the bill.
Other Charges: This may include fixed charges, meter rent, and any other applicable charges.
Total Bill: All the above components are added together to calculate the total amount due.
If you don’t want to calculate your bill or you don’t know all of above costs, just head over to Bill Calculator offered by our website.
Understanding the Components of Your FESCO Bill
When you receive your FESCO Tariff bill or FESCO Electricity Bill you see many components which are necessary to be understood. Here are some points which you need to know to understand you FESCO Bill.
Units Consumed: This section depicts the units consumed during a month.
Fixed Charges: A set fee that covers the cost of maintaining the electrical connection.
Energy Charges: The cost of the electricity consumed, calculated by multiplying the number of units by the tariff rate.
Fuel Price Adjustment (FPA): An adjustment to reflect changes in fuel costs.
Tariff Rationalization Surcharge (TRS): A surcharge that may be applied to bridge the gap between NEPRA and GOP tariffs2.
Taxes: Includes GST and other government-imposed taxes.
Arrears: Any unpaid amount from previous billing periods.
Late Payment Surcharge: A penalty for bills paid after the due date2.
By understanding these components, consumers can better manage their energy usage and ensure that their bills are accurate. If there are any discrepancies, customers should contact FESCO for clarification.
Energy Saving Tips
Reducing energy consumption not only benefits the environment but can also lead to significant cost savings. Here are some practical tips for reducing energy consumption:
Replace Incandescent Bulbs: Switch to LED or other energy-efficient light bulbs that consume up to 90% less energy.
Smart Power Strips: Use smart power strips to eliminate phantom loads by shutting off power to electronics when not in use.
Programmable Thermostats: Install programmable or smart thermostats to automatically adjust heating and cooling when you’re asleep or away.
Energy-Efficient Appliances: When purchasing appliances, consider both the purchase price and the annual operating cost.
Natural Light: Utilize natural light instead of artificial lighting whenever possible2.
Regular Maintenance: Perform regular maintenance on lighting and HVAC systems to ensure they operate efficiently.
Temperature Adjustment: Reduce heating temperatures by just 1°C to cut fuel consumption significantly.
Energy efficiency can lead to lower tariffs in several ways:
Reduced Demand: When energy efficiency leads to reduced consumption, it can prompt a reduction in energy prices, as there’s less need to add expensive new power generation capacity.
Flexibility: Energy efficiency increases flexibility, allowing users to take advantage of low-priced electricity and reducing the need for costly network reinforcements.
Time-of-Use Tariffs: Efficiency can encourage the use of time-of-use tariffs, aligning consumer behavior with variable electricity supply and potentially lowering costs.
Implementing these energy-saving measures can help consumers lower their energy bills and contribute to a more sustainable future. Remember, small changes can make a big difference in energy consumption and cost savings.
Net Metering and Incentives
Net metering is a billing mechanism that allows consumers who generate their own electricity from solar power or other renewable sources to feed electricity they do not use back into the grid. Here’s the latest information on FESCO’s net metering policies and incentives for using renewable energy sources in Pakistan:
Net Metering Policies
Eligibility: Only consumers with 3-phase meters installed at their premises are eligible for the net metering facility.
Inverter Requirements: The inverters must be of grid-tied type.
Capacity Limits: The maximum allowed capacity for the net metering facility is 1000 kW.
FESCO provides detailed guidelines and a checklist for net metering applications, ensuring that consumers can take advantage of this policy. Click here for the details.
Incentives for Renewable Energy
Pakistan is actively promoting the expansion of renewable energy in its electricity mix. The government has set ambitious targets to increase the share of renewable energy to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower electricity production costs. Incentives include:
Financial Support: The World Bank approved $450 million in financing to support Pakistan’s transition to renewable energy.
Policy Measures: The government’s Alternative and Renewable Energy Policy 2019 aims to increase the share of variable renewable energy (VRE) in the electricity mix.
Investment Opportunities: Investment in renewables is encouraged as it can save expenditure on oil imports and incentivize business with favorable terms.
These policies and incentives are designed to foster a sustainable energy future for Pakistan, making renewable energy a more attractive and viable option for consumers and businesses alike.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About FESCO Tariff Rates
What are the current residential tariff rates for FESCO?
The residential tariff rates are structured into different slabs based on the amount of electricity consumed. The rates increase as the consumption goes higher, encouraging energy conservation.
How is the commercial tariff different from the residential tariff?
Commercial tariffs are generally higher than residential tariffs and may include different fixed charges and energy charges based on the type of commercial activity and the scale of operation.
Can I reduce my tariff rate by using less electricity?
Yes, by consuming less electricity, especially during peak hours, you can reduce your energy charges. FESCO’s tariff structure is designed to reward lower consumption with lower rates.
What is a fixed charge on my FESCO bill?
A fixed charge is a set fee that covers the cost of maintaining the electrical connection to your property. This charge is applied regardless of how much electricity you use.
Are there any incentives for using renewable energy sources?
FESCO and the Pakistani government offer various incentives for using renewable energy sources, such as net metering policies that allow you to feed surplus energy back into the grid.
How can I apply for net metering with FESCO?
To apply for net metering, you need to have a 3-phase meter installed at your premises and use a grid-tied inverter. The maximum allowed capacity for net metering is 1000 kW.
What is a Fuel Price Adjustment (FPA) on my bill?
The Fuel Price Adjustment is a charge or credit on your bill that reflects the fluctuations in fuel prices used for electricity generation. It ensures that consumers pay a fair price for the energy they use.
How often do FESCO tariffs change?
FESCO tariffs can change based on various factors, including changes in fuel costs, regulatory decisions, and economic conditions. It’s important to stay updated with the latest tariff announcements from FESCO.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the intricacies of FESCO’s tariff system for both residential and commercial customers. We’ve delved into the structure of tariffs, the billing process, and the importance of understanding these elements to manage energy consumption effectively.
Call to Action
After thoroughly reading this article, you should:
Review Your Tariff: Check your latest FESCO bill to understand which tariff category you fall under and how your energy usage is being charged.
Contact FESCO: If you have any questions or need further clarification about your tariff rates or energy billing, don’t hesitate to reach out to FESCO’s customer support.
Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with any changes in tariff rates and policies by regularly visiting FESCO’s official website or subscribing to their updates.
Go Green: Consider investing in renewable energy solutions for your home or business and explore the benefits of net metering.
By staying proactive and informed, you can ensure that you’re making the most cost-effective and environmentally friendly energy choices. Take the first step today towards a more sustainable and energy-efficient tomorrow.